Introduction
The shift towards renewable aromatics in the fuel industry is gaining momentum, and for good reason. Not only does it reduce the ecological impact of transportation fuels, but it also enhances air quality by addressing the health hazards associated with common gasoline constituents like benzene.
In this article, we will explore the various strategies and innovations in the renewable fuels industry that are driving this transition. From the optimization of refinery capacities to the production of bio-based aromatics and the use of highly oxygenated organic molecules, we will delve into the technical insights and analysis behind these advancements. Join us as we uncover the promising future of renewable aromatics and its potential to revolutionize the fuel landscape.
Aromatics in Reducing Toxic Gasoline Aromatics
The shift towards renewable aromatics, derived from sustainable biomass or waste, is a promising strategy in reducing the ecological impact of transportation fuels and enhancing air quality. This transition addresses the environmental and health hazards associated with common gasoline constituents like benzene.
In the refining industry, it has been found that expanding existing refineries is more economical than constructing new ones, as seen in the United States where overall refinery capacity has increased while the number of operating refineries has decreased. However, this strategy's viability is dependent on the refinery's size and scale.
Smaller refineries often struggle with higher operational costs and lower competitiveness due to a lack of economies of scale and upgrade capacity. This reality has led to the closure of less competitive refineries and the exploration of renewable fuel production options.
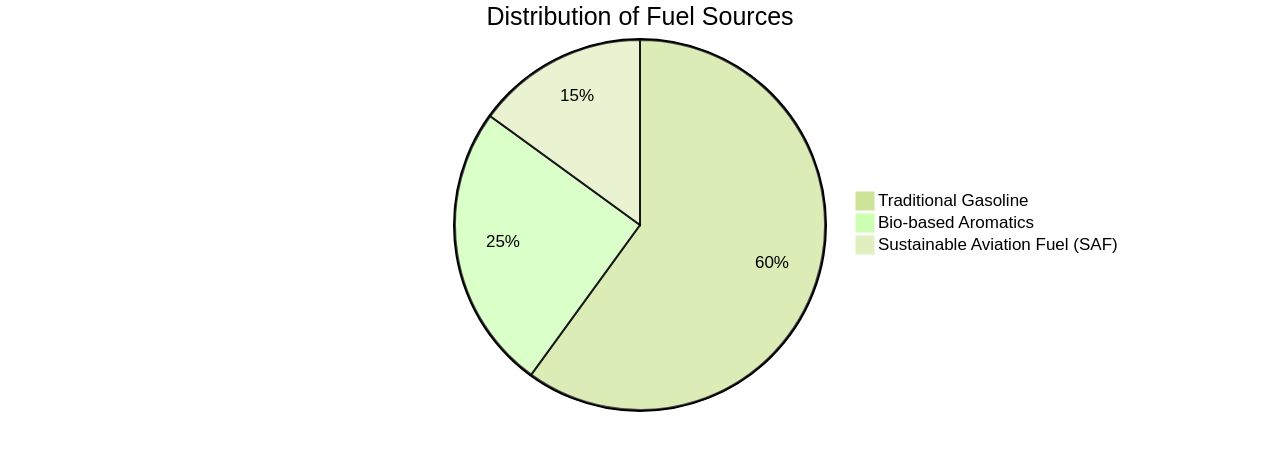
In the aviation sector, the need for aromatics in fuel has traditionally limited the use of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). However, breakthroughs in the production of bio-based aromatics have allowed for greater use of SAF.
Several airlines, including United Airlines, Emirates Airline, and Virgin Atlantic, have tested the potential of using 100% SAF. Moreover, the processing of crude oil results in heavy residues (HRs), which are typically used as low-cost fuel for ships or power plants due to their challenging upgrade process. The gasification process, which converts these residues into syngas, presents a promising alternative for increasing their market value. Furthermore, the chemical sector has made significant strides in using light to convert carbon and carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide, offering a greener approach to the carbon-intensive methods typically used. This development has wide-ranging applications, from the synthesis of acetic acid and methanol to the packaging of fresh meat products. Overall, the move towards renewable aromatics and the optimization of refinery capacities are crucial steps towards a more sustainable fuel landscape, yielding significant improvements in air quality and human health.
Formation of Highly Oxygenated Organic Molecules from Aromatic Compounds
The pathway to a sustainable future is paved by the potential of aromatic compounds serving as renewable feedstocks for biofuel, chemicals, and material production. The transformation of these renewable sources into highly oxygenated organic molecules enhances the value of aromatics and promotes resource efficiency.
Key to achieving this is the process of catalytic hydrogenation which activates the highly stable carbon-oxygen bonds in CO2, generating a variety of hydrocarbon compounds. This process has been adapted from the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, originally designed for the hydrogenation of carbon monoxide, by substituting CO with CO2.
The enzyme styrene oxide isomerase, mimicking the Meinwald reaction biologically, has been identified as a potent method for generating valuable chemicals and drug precursors from aromatics in an environmentally friendly manner. This highlights the instrumental role of aromatics in reducing pollution from synthetic chemistry processes, thereby promoting 'green' chemistry.
This aligns with oleochemistry, a field that utilizes renewable resources to produce valuable products, reducing dependence on finite fossil resources and adhering to the principles of green chemistry. In the quest for a more sustainable and eco-friendly chemical industry, the innovative use of aromatic compounds as renewable feedstocks in combination with advancements in oleochemistry is promising. For instance, the gas-phase preparation of naphthalene offers a versatile concept for the reaction of combustion and propargyl radicals with aromatic radicals, providing a resourceful source of aromatics in high temperature environments. This presents an opportunity for the industry to evolve towards a more sustainable future.

Innovations in Aromatics for Sustainable Future
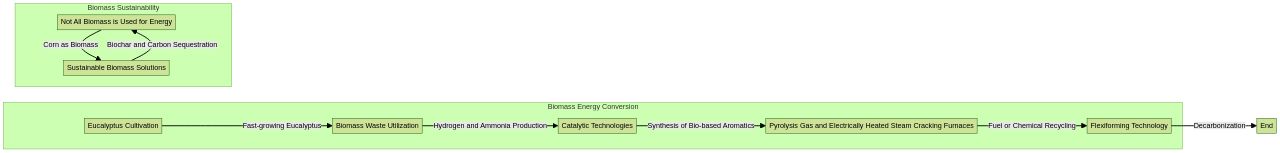
The energy sector is witnessing a rising interest in renewable aromatics, offering an opportunity to profoundly impact the sustainable energy landscape. Biomass energy conversion is a significant contributor, accounting for nearly 70% of global renewable energy production.
Countries like Brazil exemplify this, where biomass contributes 25.5% to the domestic energy supply, highlighting the untapped potential of biomass waste for valuable energy products like hydrogen and ammonia. The biomass supply chain, a burgeoning sector, can be boosted by cultivating fast-growing eucalyptus in the Southern U.S., offering a potential low-cost biomass source.
In the catalytic technologies domain, leading research initiatives are being driven by institutions such as the CAT Catalytic Center at RWTH Aachen, Germany, and the University of Stuttgart's Technology Transfer Initiative. These innovations could potentially rival the cost-effectiveness of fossil fuels.
Bio-based synthesis methods, including bio-based aromatics production, can offer a feasible solution for global aviation decarbonization. This game-changing development allows aircraft to operate on larger quantities of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), even up to 100% SAF.
The energy content of pyrolysis gas, generated by Ecomation technology, equals or even surpasses that of natural gas, positioning it as a promising candidate for fuel or chemical recycling. Furthermore, the advent of electrically heated steam cracking furnaces can potentially curtail CO2 emissions by at least 90% compared to traditional processes. This technology seeks to replace conventional fuels used for high production process temperatures with renewable electricity. In this context, Unifuel.tech introduces its Flexiforming technology, enabling operators to set their decarbonization pace. Deployed in an idle hydrotreater or reformer, it can lead to reduced capital expenditure and carbon intensity. Unifuel.tech, a subsidiary of Universal Fuel Technologies, assures a response within 24 hours when provided with information about feeds, target products, and existing facilities, offering an optimal application for Flexiforming.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the shift towards renewable aromatics in the fuel industry is a promising strategy to reduce ecological impact and enhance air quality. Optimizing refinery capacities and exploring bio-based aromatics production are crucial steps towards a more sustainable fuel landscape.
Breakthroughs in highly oxygenated organic molecules derived from aromatic compounds offer resource efficiency and promote 'green' chemistry. Innovations in renewable aromatics, such as biomass energy conversion and bio-based synthesis methods, have the potential to revolutionize the energy sector and contribute to global aviation decarbonization. With continued research and development, renewable aromatics can play a vital role in shaping a cleaner and healthier future.
Join Universal Fuel Technologies today and be a part of the renewable aromatics revolution!




