Introduction
Aviation fuel plays a crucial role in powering aircraft and enabling commercial and private flights. However, the pricing structure of aviation fuel is complex and influenced by various factors.
In this article, we will explore the cost factors of aviation fuel, including the impact of sustainable aviation efforts, airlines' fuel conservation measures, market conditions, and the role of crude oil prices. We will also delve into the influence of refining and distribution costs, taxes and duties, market demand and competition, as well as environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives. Join us as we provide technical insights and analysis into the intricate world of aviation fuel pricing.
Understanding the Cost Factors of Aviation Fuel
Aviation fuel, a key component in the airline industry, not only powers aircraft but also facilitates commercial and private flights in reaching their destinations. The pricing structure of aviation fuel is a complex equation that offers valuable insights into the various factors influencing its cost.
For instance, the introduction of levies on air fares to support the use of sustainable aviation fuel showcases how decarbonisation efforts within the industry can impact travel costs. The levy's rate is influenced by aspects such as flight duration and passenger class.
This initiative exemplifies how the shift towards a greener aviation industry can affect fuel pricing. Moreover, airlines' responses to fuel price changes can have significant implications for both the companies and society, especially in relation to climate change.
Fuel conservation measures adopted by airlines can contribute to reduced emissions, thus impacting the cost of aviation fuel. For instance, IndiGo, a leading Indian airline, introduced a fuel charge on both domestic and international routes in response to surges in Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) prices.
This move illustrates the effect of fuel price hikes on airlines' operating expenses and consequently, ticket prices. Furthermore, market conditions such as oil price fluctuations and production cuts can lead to increased fuel costs. For instance, a 25% increase in oil prices in the first half of the year resulted in a rise in fuel costs, impacting airlines' operating expenses. Additionally, a near 23% rise in jet fuel prices within a month, as indicated by International Air Transport Association (IATA) and S&P Global Commodity Insights data, underscores the volatility of the aviation fuel market. In conclusion, the pricing of aviation fuel is a complex interplay of various factors, including efforts towards sustainable air travel, airlines' fuel conservation measures, and market dynamics.
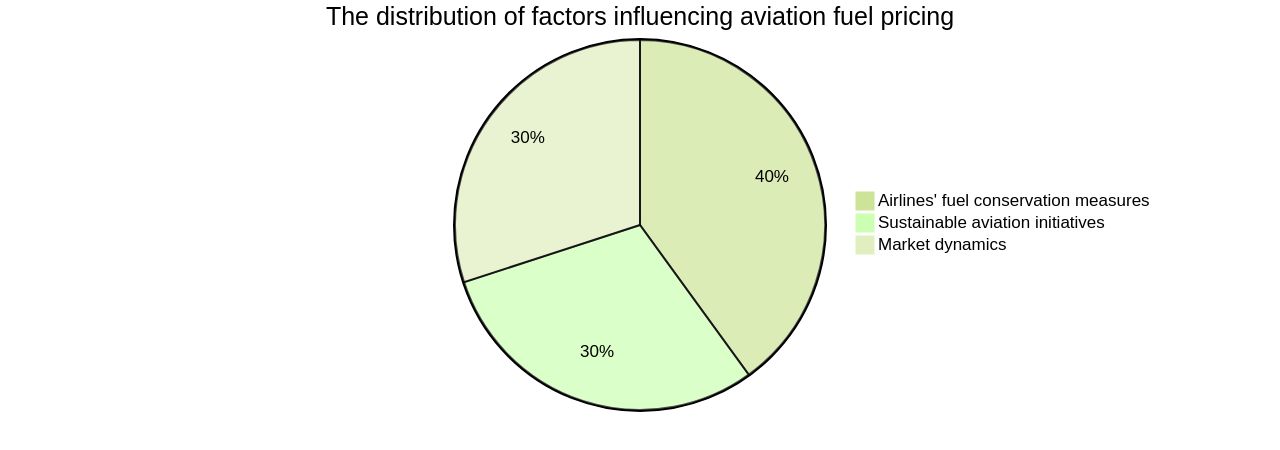
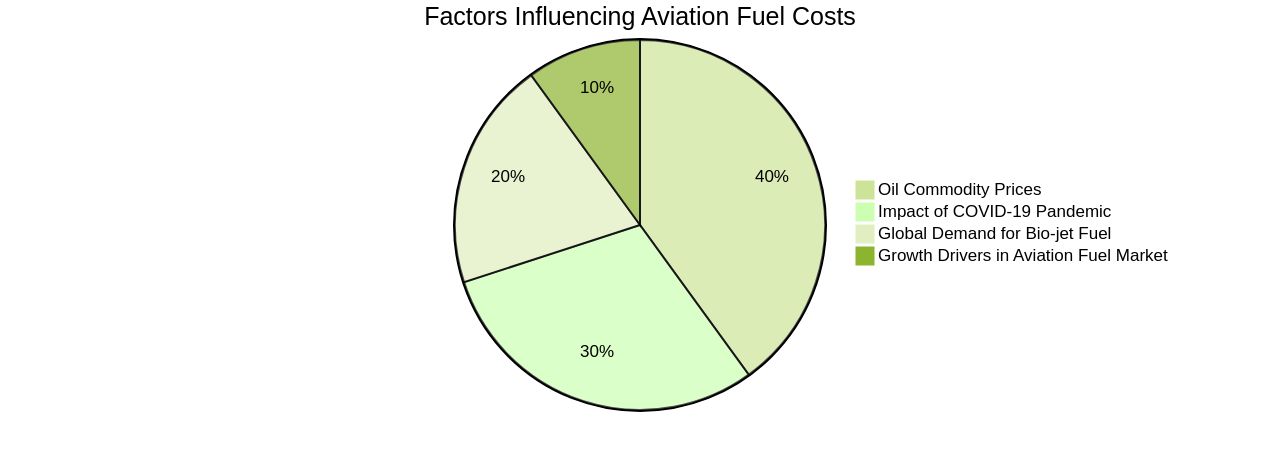
Key Factors Influencing Aviation Fuel Prices
Aviation fuel costs, inherently volatile, are influenced by a myriad of factors. For instance, the recent surge in oil commodity prices has been reflected in the aviation sector, with major airlines like United Airlines, Delta, and American experiencing increased fuel costs since the start of 2023. This trend is expected to continue, potentially impacting fare prices and airline profits.
Another significant influence is the global demand for aviation fuel, specifically bio-jet fuel. As the industry strives for sustainable air travel and reduced pollution, bio-jet fuel has seen increased demand, contributing to market growth. However, the high costs associated with these fuels could pose a challenge to progress.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact, with travel restrictions leading to decreased passenger numbers and disrupted supply chains due to mining restrictions, causing fuel price fluctuations. Nonetheless, as restrictions ease and activities resume, the market is likely to recover. Moreover, the global aviation fuel market is expected to grow, driven by factors such as better fuel-burning efficiency, the rise in international trade, and global industrial production.
This growth is most prominent in the Asia Pacific region, with a market value of USD 63.94 billion in 2021, attributed to numerous developing countries and eased travel restrictions. Lastly, airlines' capital stock, comprising long-lived, durable aircraft, offers a unique approach to studying fuel conservation efforts at a highly disaggregated level. Changes in airline operations aimed at conserving fuel could potentially lower emissions, contributing to the sector's sustainability goals.
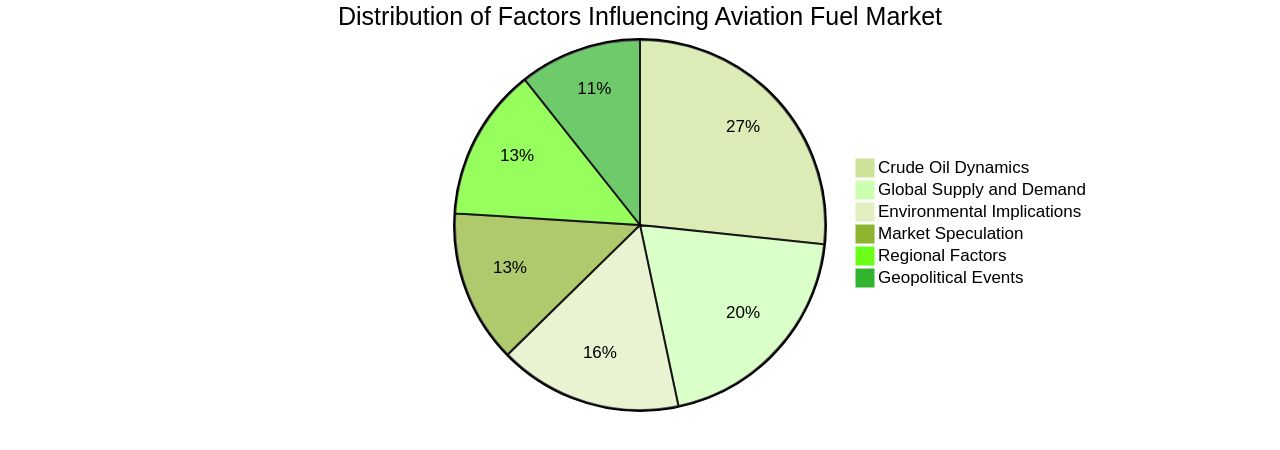
Crude Oil Prices
The aviation fuel market is intricately tied to the dynamics of the crude oil market, with the cost of the latter being a key determinant of the former. Changes in global crude oil supply and demand, market speculation, and geopolitical events all play pivotal roles in this context.
For instance, recent unilateral production cuts by Saudi Arabia and Russia, amounting to 1.3 million barrels per day, have resulted in a significant surge in oil prices. This has inevitably rippled into the aviation fuel market, with jet fuel prices seeing a nearly 23% rise in less than a month.
However, the effects of these fluctuations on the aviation industry are not uniform. Some airlines, like United Airlines, have seen their stock rise by 30% year-to-date, despite the rising fuel costs.
Others, like Alaska Airlines, are grappling with maintaining their revenue outlook in light of the escalating fuel prices. This has even led to discussions around reconsidering fuel hedging strategies among several airlines.
Moreover, the aviation industry is also grappling with the environmental implications of fuel consumption. Airlines are increasingly looking at ways to conserve fuel as a path towards lower emissions. There is also a growing demand for bio-jet fuel as a means to mitigate pollution levels and ensure sustainable air travel. Finally, regional factors also play a role in shaping the aviation fuel market. For example, the Asia Pacific region, with its numerous developing countries and burgeoning air travel market, has shown significant resilience and growth, even in the face of fluctuating fuel prices. In contrast, the North American market has seen a spike in air traffic, which is expected to fuel product demand.
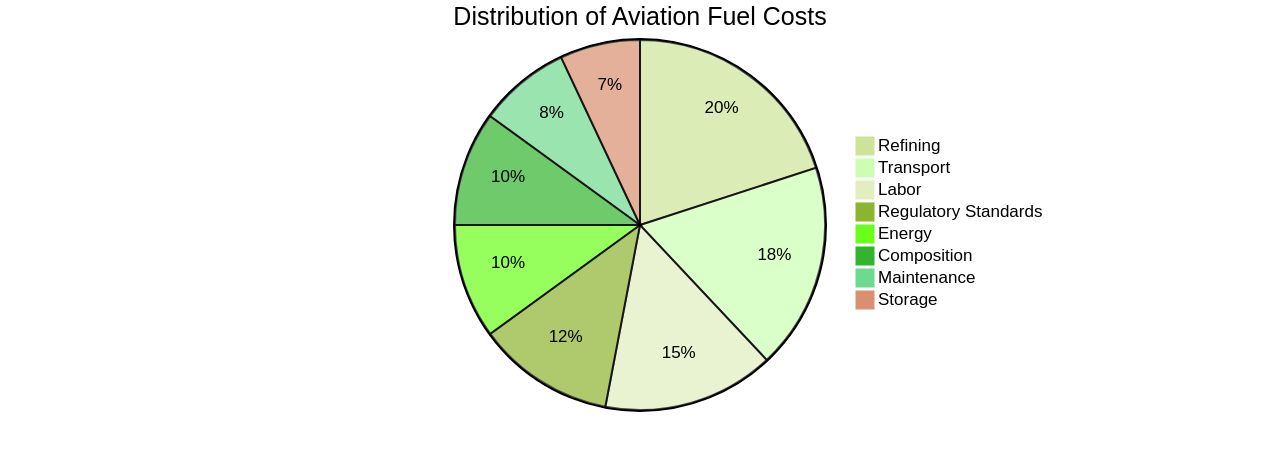
Refining and Distribution Costs
The valuation of aviation fuel isn't solely dependent on the crude oil price but also heavily influenced by the refining process and distribution logistics. Transforming crude oil into aviation fuel is a sophisticated procedure, incurring substantial expenses, including labor, energy, maintenance, and adherence to regulatory standards.
The experience across the refining industry indicates that enhancing the capacity of existing refineries is economically more viable than establishing new ones. However, the viability of capacity increment is dependent on the size and scale of refineries.
Larger refineries have a scale advantage, while smaller ones lack the economies of scale, making them less competitive and more expensive to operate. Additionally, the transport and storage of aviation fuel add more costs, considering the logistics, infrastructure, and safety measures involved.
The aviation fuel composition also contributes to the cost. About 75-90% of it comprises aliphatic molecules, similar to diesel fuels, with the remaining 10-25% being aromatic molecules, which are essential for setting the physical and combustion properties of the overall mixture.
The global aviation fuel market is anticipated to grow due to the increasing demand for bio-jet fuel aimed at reducing pollution levels and ensuring sustainable air travel. However, the high cost associated with aircraft fuels might hinder market progress.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic negatively impacted the market due to travel restrictions, causing a drop in passenger visits and hampering the demand for air travel. This also led to fuel price fluctuations due to mining activity restrictions.
The International Civil Aviation Organization has set a goal for the industry to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050. Changes in airline operations directed toward conserving fuel can be a significant path toward lower emissions. The promise of sustainable aviation fuels in regions like the Great Lakes and the Rocky Mountain region signifies a new era in aviation, marking a cleaner, greener aviation industry. However, the need for aromatics in aviation fuel currently limits the percentage of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) that can be added. Yet, a new process producing bio-based aromatics has made it possible to fuel aircraft with greater volumes of SAF, including 100% SAF. This has been tested by United Airlines, Emirates Airline, Gulfstream, Bell Textron, and now Virgin Atlantic, marking the first 100% SAF, trans-Atlantic crossing by a commercial airline. The SAF offers the most practical solution to decarbonizing global aviation because it can be a “drop-in” solution, requiring no modification of global aircraft fleets, airports, and fueling infrastructure. The future of aviation fuel depends on the industry’s ability to adapt to these changes and advancements.
Taxes and Duties
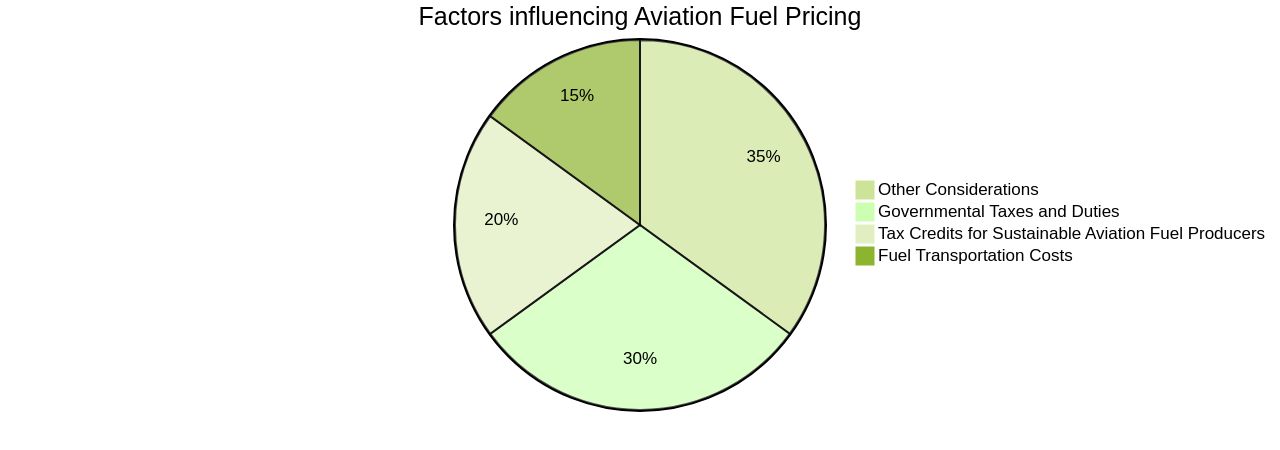
Aviation fuel pricing is profoundly influenced by various factors, among which governmental taxes and duties are significant. The impact of these charges varies globally due to the diverse tax policies and regulations in different countries, leading to regional price disparities.
For instance, sustainable aviation fuel producers are set to benefit from tax credits ranging from $1.25 to $1.75 per gallon, a strategy approved by the U.S. Congress to incentivize cleaner energy production and reduce the cost of sustainable fuel. Conversely, international flights may experience added tax burdens when crossing borders, further complicating the overall cost of aviation fuel.
For example, the EU prohibits fuel tax on international flights originating from within its jurisdiction but allows taxation on domestic flights, a policy yet to be embraced by any member states. Furthermore, fuel transportation costs significantly contribute to the final fuel price.
A study used data from Argus Media and Bloomberg to estimate the costs of transporting light crude oil and three refined products, including jet fuel, from the Gulf Coast to various East Coast points. The results revealed a price difference of approximately $2.00 a barrel for the refined products, implying that domestic transport is more efficient than international trade. The aviation industry is currently responsible for 2% of annual global energy-related emissions, and the demand for flying is predicted to grow, potentially tripling emissions by 2050. Therefore, the implementation of aviation fuel taxes and sustainable fuel strategies is a critical consideration in achieving a balance between economic growth and environmental preservation.
Market Demand and Competition
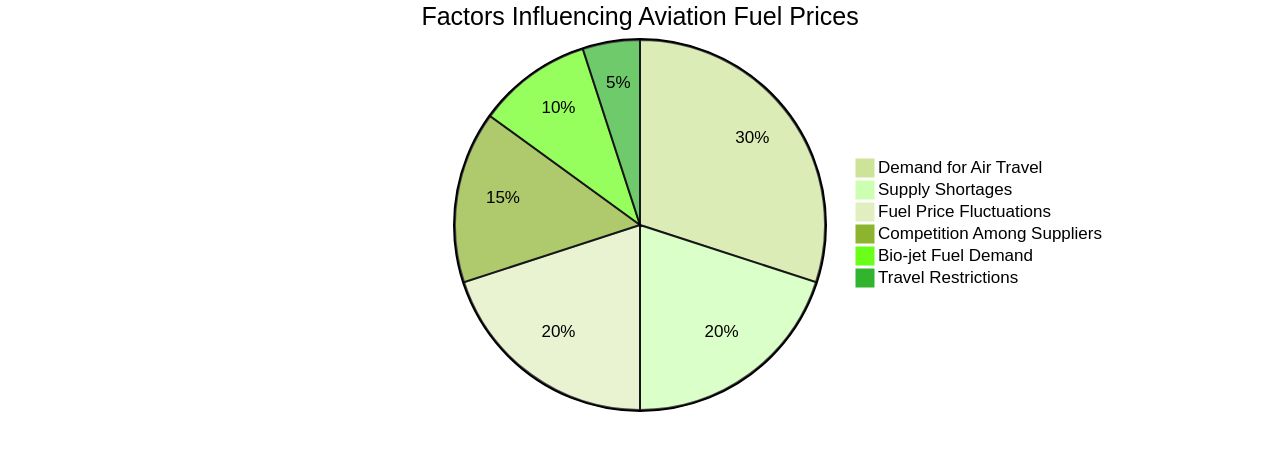
Aviation fuel, much like any other market-driven commodity, experiences price variations influenced by several factors. The demand for air travel, particularly during high travel seasons, can escalate aviation fuel prices.
Besides, the competition among aviation fuel suppliers and distributors also plays a significant role in shaping pricing strategies as they endeavor to attract customers and maintain their market share. The global aviation fuel market, worth USD 63.94 billion in 2021, is poised for expansion, driven by an increasing demand for bio-jet fuel which promises to reduce pollution levels and ensure sustainable air travel.
However, the high costs associated with aircraft fuels may impede market growth. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the market was adversely affected due to travel restrictions.
Reduced passenger visits impinged on the demand for air travel, negatively impacting the industry. Moreover, restrictions on mining activities led to supply shortages and fuel price fluctuations.
The commercial segment of the market is anticipated to lead due to rising air traffic in developing regions and the rapid development of commercial airlines. In particular, the Asia Pacific region is projected to dominate the aviation fuel market share owing to the presence of numerous developing countries and eased transport and travel restrictions. In North America, increasing air traffic is expected to augment product demand. Furthermore, airlines are adjusting their operations to conserve fuel, a move that has implications for emissions and climate change. These adjustments are influenced by fuel price changes and are part of a broader effort to manage the airline's capital stock, which includes long-lived, durable aircraft. The industry's response to fuel prices highlights the dynamics of aviation fuel pricing and its wide-ranging impacts.
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Initiatives
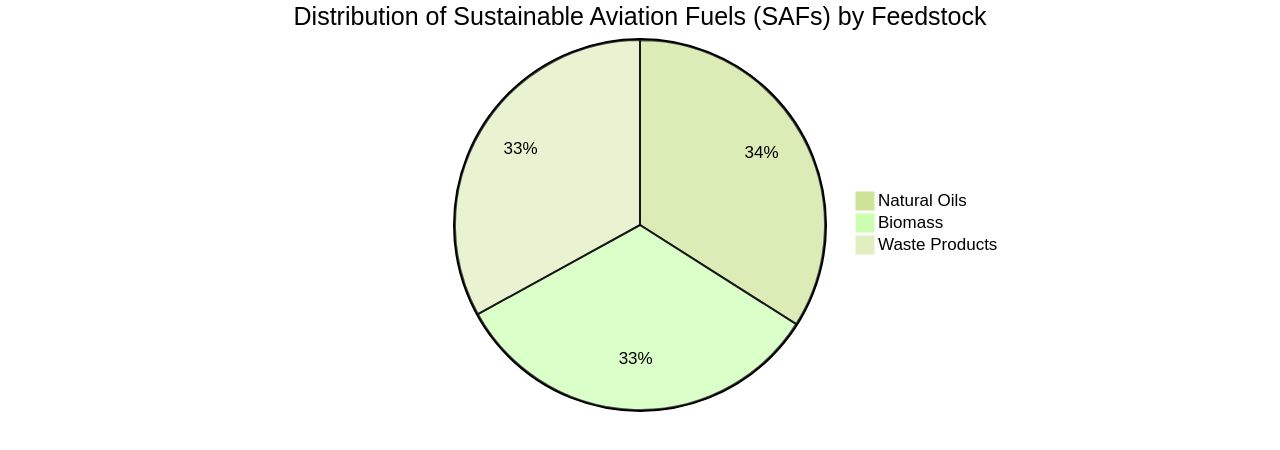
In the face of the escalating demand for emission reduction, the aviation sector is pivoting towards Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs). These fuels, derived from various feedstocks like biomass, waste products, and natural oils, are becoming increasingly important, particularly given the current challenges with electrification and green hydrogen for long-haul flights. Despite the increase in the usage of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) in Europe, the UK, and the USA, there is a discrepancy between the supply and demand due to production limitations. Can you please tell me how much is aviation fuel per gallon?
Added to this are the high production costs associated with feedstock availability and scaling issues. However, the aviation industry remains committed to sustainability, with the affordability and sustainability of Safe being important factors. By the way, could you please let me know how much is aviation fuel per gallon? There is also the pressing need to reduce CO2 emissions without adversely affecting the passenger experience or increasing exposure to other pollutants.
Achieving the goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 will depend on several factors, such as the progress of genuinely sustainable aviation fuels and positive policy incentives. By the way, do you happen to know how much aviation fuel costs per gallon? However, Unifuel. Tech is offering a solution to decelerate the industry's carbon footprint with their Flexiforming technology. Do you know how much aviation fuel costs per gallon?
This technology can be implemented in an idle hydrotreater or reformer, significantly reducing capital expenditure and carbon intensity. Do you know the cost of aviation fuel per gallon? Unifuel.tech's approach provides personalized solutions, taking into account the operator's feed, target products, and existing facilities. By the way, do you know how much aviation fuel costs per gallon? Thus, the economics of aviation fuel are set to witness significant shifts as sustainability moves into the limelight.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pricing of aviation fuel is influenced by factors such as sustainable aviation efforts, airlines' conservation measures, market conditions including crude oil prices, refining and distribution costs, taxes and duties, market demand and competition, as well as environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives. Efforts towards sustainable air travel impact travel costs, while fuel conservation measures contribute to reduced emissions and affect the cost of aviation fuel.
Market conditions, such as oil price fluctuations and production cuts, can lead to increased fuel costs. The dynamics of the crude oil market play a pivotal role in aviation fuel prices.
Refining and distribution costs, along with taxes and duties imposed by governments, heavily influence pricing. Market demand and competition among suppliers shape pricing strategies.
The industry's shift towards Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs) is driven by environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives. However, challenges such as production constraints and high costs hinder the scaling up of SAF usage. In summary, the pricing structure of aviation fuel is complex and influenced by various interconnected factors. Adapting to these factors will be crucial for achieving a balance between economic growth and environmental preservation in the aviation industry.




