Introduction
The aviation industry heavily relies on the management and cost of fuel resources, with jet fuel prices significantly impacting profitability and cost structures. In this article, we will provide a comparative analysis of current jet fuel prices and explore the factors that influence their cost.
From geopolitical events to supply-demand dynamics, we'll delve into the complex landscape of jet fuel pricing. Additionally, we will discuss the emerging role of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and its potential to revolutionize the industry's carbon reduction efforts. Join us as we navigate the technical and analytical aspects of the renewable fuels industry.
Current Jet Fuel Prices: A Comparative Analysis
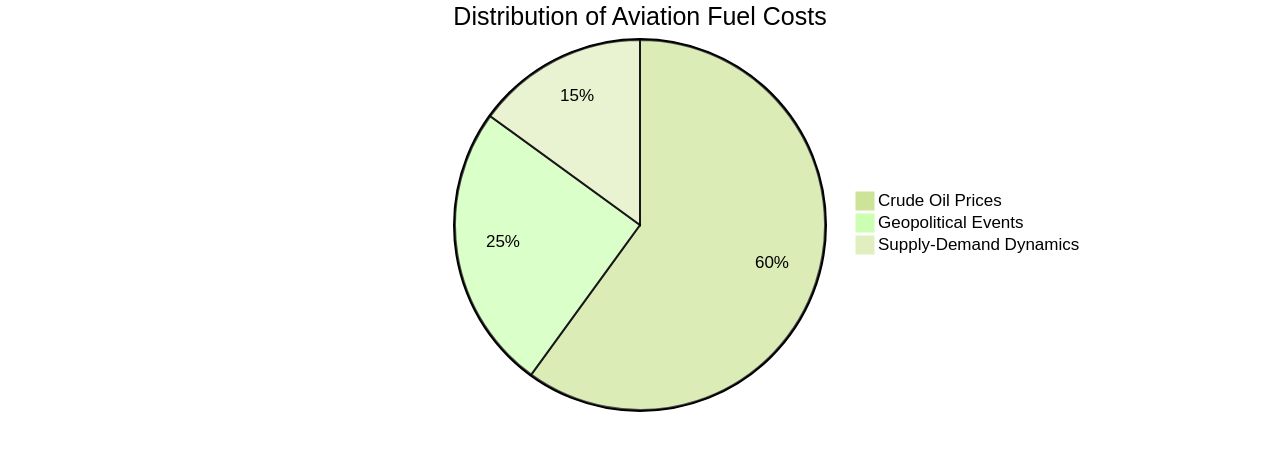
The aviation industry's economic framework is significantly influenced by the management and cost of fuel resources. Factors such as crude oil prices, geopolitical events, and supply-demand dynamics contribute to the cost of jet fuel.
This cost, in turn, profoundly impacts the profitability margins and cost structures within the industry. An example of this is the 25% surge in oil prices since the end of June, which led to a rise in fuel costs and posed challenges for airlines such as United Airlines, Delta, and American.
Jet fuel prices, which averaged $119.82 per barrel for the week ending Friday, August 4, 2023, mark a nearly 23% increase from $97.78 for the week ending July 7, 2023. This surge is not only a result of crude oil production cuts by Saudi Arabia and Russia but also reflects the strong performance of the Asia Pacific air travel market.
While operational changes aimed at fuel conservation can significantly reduce emissions, rising fuel costs and global conflicts might lead to higher fares. This could further strain consumers already grappling with high inflation, especially in the Asia Pacific region.
Here, the aviation fuel market, valued at USD 63.94 billion in 2021, is projected to grow. However, the high costs associated with aircraft fuels could pose a significant challenge.
In this evolving scenario, companies like Unifuel.tech offer innovative solutions. Their technology, flexiforming, allows operators to control their decarbonization pace. This technology can be implemented in an idle hydrotreater or reformer, thus reducing carbon intensity and capital expenditure. Such solutions could play a pivotal role in the economic landscape of the aviation industry, as jet fuel price analysis remains a critical component. Despite the challenges, current market dynamics suggest a return to profitability for a growing number of airlines. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) projects that the average operational profitability (EBIT) of the airline sector will recover to 2.8% in 2023.
Understanding the Cost of Jet Fuel: Factors Affecting the Price
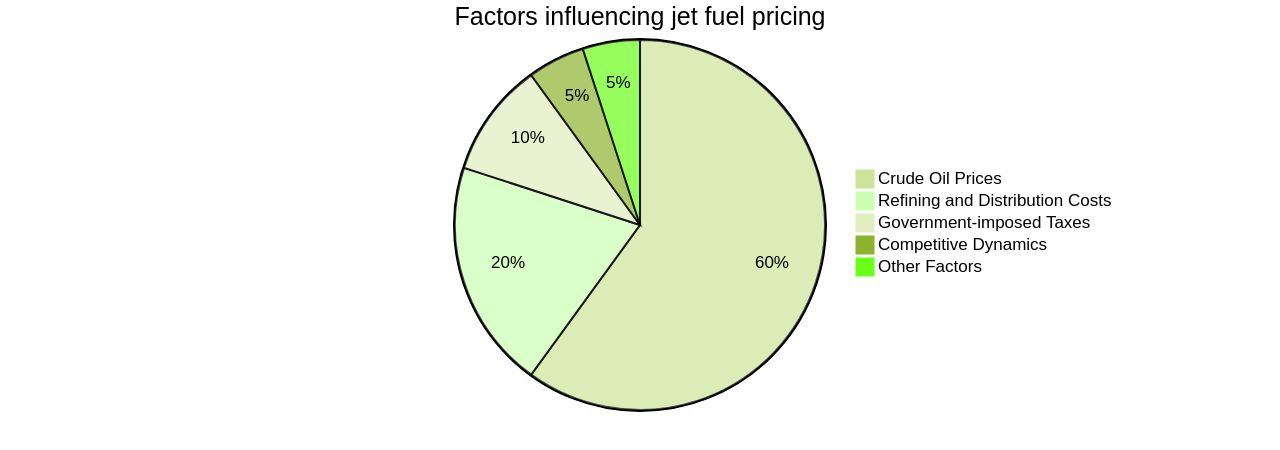
The intricacies of jet fuel pricing are influenced by various factors, with crude oil prices being the main determinant, owing to its role as the primary feedstock for jet fuel production. Refining and distribution costs, encompassing transportation and storage, also significantly contribute.
The pricing per gallon of jet fuel is impacted by government-imposed taxes, the competitive dynamics among fuel suppliers, and other elements. Recently, major airlines, including United Airlines, Delta, and American, have reported a surge in fuel costs in correlation with the climbing commodity prices for oil, leading to predictions of continuous cost increases.
This rise could potentially translate into higher fares for consumers already dealing with high inflation rates. Hydrocarbon fuels have an advantage in commercial airliners due to the space and weight limitations requiring a power source with high energy density.
For instance, today's batteries would weigh 40 times as much to provide equivalent energy to kerosene jet fuel. Additionally, meticulous planning and forecasting of the annual operating budget for business jets is crucial, taking into consideration the fluctuating prices of jet fuel, a significant line item in any aircraft budget.
The geographical destinations of flights also play a role in determining the average fuel price forecast. The aviation fuel market growth is driven by factors such as better aircraft fuel-burning efficiency, growing international trade, rising global industrial production, and an improved economic scenario. However, the high costs associated with aircraft fuels can hinder market progress. For instance, IndiGo, a major airline, reported fuel expenses as 37.15% of total expenditure in the first quarter of FY 24. The rising demand for bio-jet fuel, intended to mitigate pollution levels and ensure sustainable air travel, is likely to boost the global aviation fuel market size. Yet, the restrictions on travel during the COVID-19 pandemic negatively affected this market due to reduced passenger visits and restrictions on mining activities, leading to a lack of supply and fuel price fluctuations.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel: The Future of Ethanol?
Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), derived from renewable resources, is a potential answer to the urgent carbon reduction need in the aviation industry. However, its full potential is yet to be harnessed due to challenges like cost-efficiency and scalability of production.
The energy landscape's volatility exacerbates these challenges, testing the aviation industry's commitment to emission reduction. With no viable alternatives for long-haul flights, the dependence on SAF becomes more critical.
The increasing adoption of SAF, especially in Europe, the UK, and the USA, is surpassing its global production, causing a supply-demand imbalance. The European Green Deal's ambitious targets, aiming for significant net emission cuts by 2030 and climate neutrality by 2050, mirror the aviation industry's goal of net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
However, SAF technology is still nascent, and alternative fuels comprise less than 0.2% of the global jet fuel supply. While SAF production technologies are mostly developed, supply remains insufficient.
The economic viability of SAF feedstocks and biofuel feedstock competition from other industries continue to limit supply. Power-to-liquids (PtL) fuel, composed of synthetically produced liquid hydrocarbons, is a promising prospect, though its contribution to aviation decarbonization by 2050 may be limited.
The task of augmenting SAF production is enormous and requires a collaborative approach. Despite these challenges, the growing demand-gap presents a profitable opportunity for timely market entry by SAF producers. Unifuel.tech's Flexiforming technology provides a solution for operators to manage their decarbonization pace. This technology can be deployed in an idle hydrotreater or reformer, reducing capital expenditure and carbon intensity. By providing information about feeds, target products, and existing facilities, uni fuel. Tech can identify an optimal application for Flexiforming, potentially facilitating a more sustainable aviation industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, jet fuel prices have a significant impact on the aviation industry's profitability and cost structures. Factors such as crude oil prices, geopolitical events, and supply-demand dynamics contribute to the rising costs of jet fuel. Recent trends have shown a substantial surge in jet fuel prices, posing challenges for airlines and potentially leading to higher fares for consumers.
To address these challenges, innovative solutions like Unifuel.tech's flexiforming technology offer operators the ability to control their decarbonization pace while reducing carbon intensity and capital expenditure. Understanding the factors that affect jet fuel pricing is crucial for stakeholders in the industry. Crude oil prices, refining and distribution costs, taxes, competitive dynamics among fuel suppliers, and other elements all play a role in determining jet fuel costs.
Looking ahead, sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) derived from renewable resources holds promise for reducing carbon emissions in the aviation sector. However, challenges related to cost-efficiency and production scalability need to be addressed. Collaboration among stakeholders is crucial to accelerate SAF production and meet ambitious emission reduction targets.
In conclusion, navigating the complex landscape of jet fuel pricing requires an understanding of various factors that influence costs. Innovations in sustainable aviation fuel technology hold promise for revolutionizing carbon reduction efforts in the aviation industry. By embracing solutions like flexiforming technology offered by companies like Unifuel.tech, stakeholders can pave the way towards a more economically viable and environmentally sustainable future for aviation.
take control of your decarbonization pace and reduce carbon intensity and capital expenditure.




