Introduction
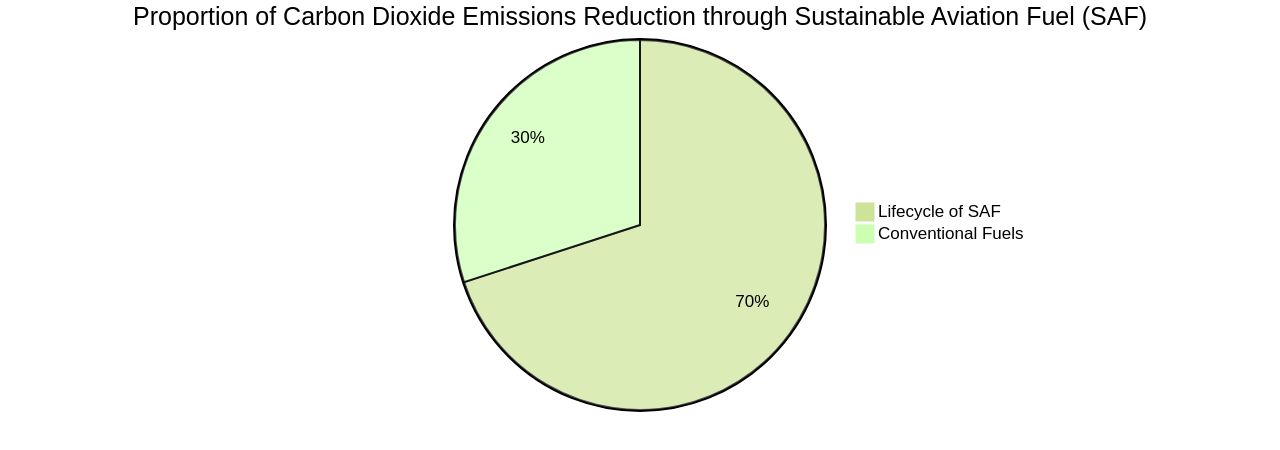
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a transformative tool in the aviation sector's fight against climate change. With the potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 80%, SAF offers a cleaner alternative to conventional fuels. However, the widespread adoption of SAF faces challenges such as a consistent fuel supply.
Additionally, while SAF plays a pivotal role in decarbonizing the aviation industry, it is not the sole solution. The development of new technologies and infrastructure will also be necessary. This article explores the benefits of SAF, the production process, and the certification and approval process, providing technical insights and analysis for readers with a deep understanding of the renewable fuels industry.
Benefits of Sustainable Aviation Fuel
According to the sustainable aviation fuel wiki, Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) plays a crucial role in the aviation sector's efforts to combat climate change. The utilization of sustainable aviation fuel wiki, also known as SAF, can result in an 80% decrease in carbon dioxide emissions throughout its lifecycle, making it a cleaner alternative to conventional fuels. Furthermore, sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) also possesses the capability to improve air quality through the reduction of the emission of detrimental pollutants like sulfur oxides and particulate matter, as mentioned on the sustainable aviation fuel wiki.
The importance of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is underscored by the International Civil Aviation Organization's ambition for the industry to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, as mentioned in the sustainable aviation fuel wiki. Considering that aviation is responsible for around 3% of worldwide CO2 emissions and is a difficult industry to make carbon-neutral, the role of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) becomes essential. For more information, you can refer to the Sustainable Aviation Fuel Wiki. The industry-wide push to expand the global SAF market, with leading airlines and companies like Airbus pledging to make their aircraft 100% SAF-capable by 2030, is evident and can be found on the sustainable aviation fuel wiki page.
However, the journey towards widespread SAF adoption is not without its obstacles. As demonstrated by the Virgin Atlantic flight from London's Heathrow to New York's JFK airport, powered by SAF, the lack of a consistent fuel supply is a significant challenge. The flight, while historic, was a one-off, underscoring the need for a reliable source of SAF to make regular, commercial flights possible.
While SAF can enable decarbonization within existing aircraft and infrastructure, it is not the sole solution. According to the sustainable aviation fuel wiki, achieving full decarbonization will require the development of new technologies and the adaptation of existing facilities. However, it is clear that SAF, with its ability to reduce emissions significantly, will play a pivotal role in the aviation industry's sustainable future.
Production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel
The production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a multifaceted process, involving the conversion of renewable feedstocks, such as biomass, waste oils, and algae, into flight-ready fuel. Key steps in this transformation include hydroprocessing, esterification, and fermentation. However, this process does present several challenges, such as feedstock availability, adhering to sustainability standards, and the need for technological advancement.
The aviation sector is largely dependent on SAF to achieve its carbon reduction goals, especially for long-haul flights where options like electrification or green hydrogen are currently not feasible. However, the global demand for SAF is predicted to surpass supply due to limited production capacities, triggering debates about cost, sustainability, and feedstock competition. Countries like Australia, a major exporter of biofuel feedstocks, could be instrumental in addressing this demand and diversifying feedstock sources.
Moreover, SAF production is also constrained by strict regulations around aviation fuels due to the specific requirements of airplane engines. The creation of a fully sustainable hydrocarbon fuel for aircraft has been a significant hurdle. However, the development of new processes that produce bio-based aromatics have now made it feasible to fuel aircraft with higher proportions of SAF, potentially up to 100%.
One such technological advancement is Flexiforming offered by Unifuel.tech. This technology enables operators to choose their decarbonization pace. It can be implemented in an idle hydrotreater or reformer, minimizing both capital expenditure and carbon intensity.
Unifuel.tech's swift response to inquiries and its ability to tailor Flexiforming applications to specific feeds, target products, and existing facilities offers a promising solution to some of the challenges in SAF production. As the aviation industry aims for carbon neutrality by 2050, SAF stands as a primary means of achieving this goal. Despite the hurdles of scaling production, developing key infrastructure, and formulating suitable policies, the future of SAF remains hopeful, driven by ongoing technological advancements and strategic shifts in the aviation sector.
Certification and Approval Process
The aviation industry is actively striving towards net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, with Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) being a critical tool to achieve this goal. The fuel undergoes rigorous certification processes to ensure its quality, safety, and compatibility with existing aircraft infrastructure.
Globally recognized bodies such as ASTM International and IATA have developed stringent standards and guidelines to ensure Saf's safety and its effectiveness in reducing carbon emissions. The aviation sector, contributing 2-3% of global CO2 emissions, views SAF as a primary solution to decarbonization challenges.
Airbus, for example, is working diligently to make its entire fleet 100% SAF-capable by 2030, while also partnering with airlines like Emirates to broaden the global SAF market. Singapore Airlines' recent acquisition of 1,000 tonnes of SAF from Neste, the world's largest SAF producer, underscores the rising industry adoption of SAF.
This fuel, derived from 100% renewable waste and residue raw materials, can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 80% over its lifecycle, further emphasizing its potential in the aviation industry's decarbonization efforts. In this context, solutions like Unifuel.tech's Flexiforming provide an innovative approach to decarbonization. Flexiforming allows operators to control their decarbonization pace and can be implemented in an idle hydrotreater or reformer, reducing both capital expenditure and carbon intensity. The company is committed to providing an optimal application for Flexiforming based on the operator's feeds, target products, and existing facilities, demonstrating a proactive approach to inquiries within 24 hours.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a crucial tool in the aviation sector's fight against climate change. With the potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 80%, SAF provides a cleaner alternative to conventional fuels and enhances air quality by reducing harmful pollutants.
However, challenges such as consistent fuel supply and the need for new technologies and infrastructure remain. The production of SAF involves converting renewable feedstocks into flight-ready fuel, with issues like feedstock availability and sustainability standards needing attention.
Certification processes ensure the quality and safety of SAF, with globally recognized bodies setting stringent standards. The rising industry adoption of SAF highlights its potential in decarbonization efforts.
While challenges persist, the future of SAF looks hopeful. Ongoing technological advancements, such as Unifuel.tech's Flexiforming, offer tailored solutions to specific feeds and existing facilities. Strategic shifts within the aviation sector also contribute to progress. In summary, SAF offers significant benefits in emissions reduction and air quality improvement. Despite challenges, the industry's commitment to SAF adoption and continuous technological advancements pave the way for a sustainable future in aviation.




